It is easy to calculate around 90 % of applications knowing only the following five parameters:
- Abzubremsende Masse (Gewicht) m [kg]
- Aufprall- oder Auffahrgeschwindigkeit vD [m/s]
- Evtl. vorhandene zusätzliche Antriebskraft F [N]
- Anzahl der Hübe oder Takte pro Stunde x [1/h]
- Anzahl Stoßdämpfer parallel n
Key to symbols used
| Symbol | Unit | Description | Symbol | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | Nm | Kinetic energy per cycle | 3ST | 1 to 3 | tall torque factor (normally 2.5) |
| W2 | Nm | Propelling force energy per cycle | M | Nm | Propelling torque |
| W3 | Nm | Total energy per cycle (W1 + W2) | I | kgm2 | Moment of Inertia |
| 1W4 | Nm/hr | Total energy per hour (W3 · c) | g | m/s2 | Acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 |
| me | kg | Effective weight | h | m | Drop height excl. shock absorber stroke |
| m | kg | Mass to be decelerated | s | m | Shock absorber stroke |
| n | Number of shock absorbers (in parallel) | L/R/r | m | Radius | |
| 2v | m/s | Velocity at impact | Q | N | Reaction force |
| 2vD | m/s | Impact velocity at shock absorber | μ | Coefficient of friction | |
| ω | rad/s | Angular velocity at impact | t | s | Deceleration time |
| F | N | Propelling force | a | m/s2 | Deceleration |
| c | 1/hr | Cycles per hour | α | ° | Side load angle |
| P | kW | Motor power | β | ° | Angle of incline |
Note:
When using several shock absorbers in parallel, the values (W3), (W4) and (me) are divided according to the number of units used.
|
Reaction force Q [N] Q = (1,5 · W3) / s |
Stopping time t [s] t = (2,6 · s) / vD |
Deceleration a [m/s2] a = (0,75 · vD2) / s |
Approximate values assuming correct adjustment. Add safety margin if necessary. (Exact values will depend upon actual application data and can be provided on request.)
Applications
| Application | Formulae | Example | |
|---|---|---|---|
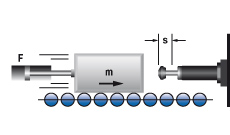
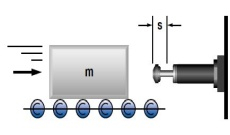
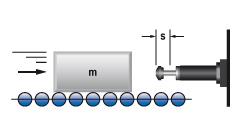
1. Mass without propelling force
|
W1 = m · v2 · 0,5
W2 = 0
W3 = W1 + W2
W4 = W3 · x
vD = v
me = m
|
m = 100 kg W1 = 100 · 1,52 · 0,5 = 113 Nm |
|
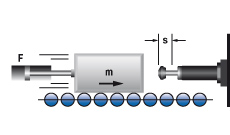
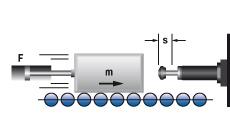
2. Mass with propelling force
|
W1 = m · v2 · 0,5
W2 = F · s
W3 = W1 + W2
W4 = W3 · x
vD = v
me = (2 · W3) / vD2
2.1 bei senkrechter Bewegung nach oben
W2 = (F – m · g) · s
2.2 bei senkrechter Bewegung nach unten
W2 = (F + m · g) · s
|
m = 36 kg
1v = 1,5 m/s
F = 400 N
x = 1000 1/h
s = 0,025 m (gewählt)
W1 = 36 · 1,52 · 0,5 = 41 Nm
W2 = 400 · 0,025 = 10 Nm
W3 = 41 + 10 = 51 Nm
W4 = 51 · 1000 = 51000 Nm/h
me = 2 · 51 : 1,52 = 45 kg
1 v is the fi nal impact velocity of the mass:
With pneumaticallypropelled systems this can be 1.5 to 2 times the average velocity. Please take this into account when calculating energy. |
|
3. Mass with motor drive
|
W1 = m · v2 · 0,5
W2 = (1000 · P ·HM · s) / v
W3 = W1 + W2
W4 = W3 · x
vD = v
me = (2 · W3) / vD2
|
m = 800 kg W1 = 800 · 1,22 · 0,5 = 576 Nm motor, coupling and gearbox into calculation for W1 |
|
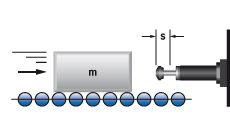
4. Mass on driven rollers
|
W1 = m · v2 · 0,5
W2 = m · μ · g · s
W3 = W1 + W2
W4 = W3 · x
vD = v
me = (2 · W3) / vD2
|
m = 250 kg W1 = 250 · 1,52 · 0,5 = 281 Nm |
|
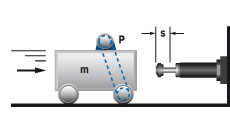
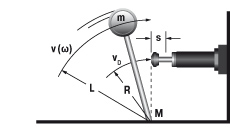
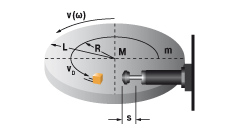
5. Swinging mass with propelling force
|
W1 = m · v2 · 0,5 = 0,5 · J · ω2
W2 = (M · s) / R
W3 = W1 + W2
W4 = W3 · x
vD = (v · R) / L = ω · R
me = (2 · W3) / vD2
|
m = 20 kg W1 = 20 · 12 · 0,5 = 10 Nm |
|
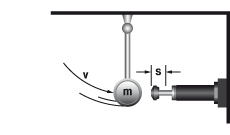
6. Free falling mass
|
W1 = m · g · h
W2 = m · g · s
W3 = W1 + W2
W4 = W3 · x
vD = √2 · g · h
me = (2 · W3) / vD2
|
m = 30 kg W1 = 30 · 0,5 · 9,81 = 147 Nm |
|
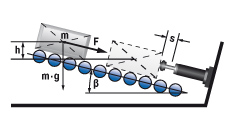
6.1 Mass rolling/sliding down incline
|
W1 = m · g · h = m · vD2 · 0,5
W2 = m · g · sinβ · s
W3 = W1 + W2
W4 = W3 · x
vD = √2 · g · h
me = (2 · W3) / vD2
6.1a bei senkrechter Bewegung nach oben
W2 = (F – m · g· sinβ) · s
6.1b bei senkrechter Bewegung nach unten
W2 = (F + m · g· sinβ) · s
|
m = 500 kg W1 = 500 · 9,81 · 0,1 = 490,5 Nm |
|
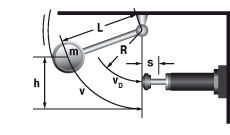
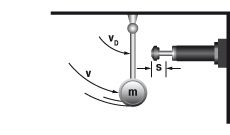
6.2 Mass free falling about a pivot point
|
W1 = m · g · h
W2 = 0
W3 = W1 + W2
W4 = W3 · x
vD = √2 · g · h · (R / L)
me = (2 · W3) / vD2
tan α = s / R
|
m = 50 kg W1 = 50 · 9,81 · 1 = 490,5 Nm |
|
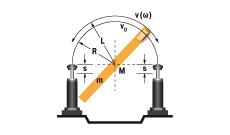
7. Rotary index table with propelling torque
|
W1 = m · v2 · 0,25 = 0,5 · J · ω2
W2 = (M · s) / R
W3 = W1 + W2
W4 = W3 · x
vD = (v · R) / L = ω · R
me = (2 · W3) / vD2
|
m = 1000 kg W1 = 1000 · 1,12 · 0,25 = 303 Nm |
|
8. Swinging arm with propelling torque (uniform weight distribution)
|
W1 = m · v2 · 0,17 = 0,5 · J · ω2
W2 = (M · s) / R
W3 = W1 + W2
W4 = W3 · x
vD = (v · R) / L = ω · R
me = (2 · W3) / vD2
|
J = 56 kgm2 W1 = 0,5 · 56 · 12 = 28 Nm |
|
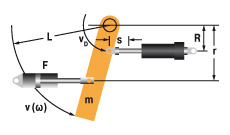
9. Swinging arm with propelling force (uniform weight distribution)
|
W1 = m · v2 · 0,17 = 0,5 · J · ω2
W2 = (F · r · s) / R = (M · s) / R
W3 = W1 + W2
W4 = W3 · x
vD = (v · R) / L = ω · R
me = (2 · W3) / vD2
|
m = 1000 kg W1 = 1000 · 22 · 0,17 = 680 Nm |
|
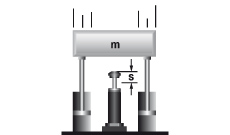
10. Mass lowered at controlled speed
|
W1 =m · v2 · 0,5
W2 = m · g · s
W3 = W1 + W2
W4 = W3 · x
vD = v
me = (2 · W3) / vD2
|
m = 6000 kg W1 = 6000 · 1,52 · 0,5 = 6750 Nm |
|
Effective Weight (me)
The effective weight (me) can either be the same as the actual weight (examples Aand C), or it can be an imaginary weight representing a combination of the propelling force or lever action plus the actual weight (examples B and D).
| Einsatzfall | Beispiel |
|---|---|
A Mass without propelling force
|
m = 100 kg
vD = v = 2 m/s
W1 = W3 = 200 Nm
me = (2 · 200) / 4 = 100 kg
FORMULA: ME = M
|
B Mass with propelling force
|
m = 100 kg
F = 2000 N
vD = v = 2 m/s
s = 0,1 m
W1 = 200 Nm
W2 = 200 Nm
W3 = 400 Nm
me = (2 · 400) / 4 = 200 kg
FORMEL: ME = (2 · W3) / VD2
|
C Mass without propelling force direct against shock absorber
|
m = 20 kg
vD = v = 2 m/s
W1 = W3 = 40 Nm
me = (2 · 40) / 22 = 20 kg
FORMEL: ME = M
|
D Mass without propelling force with mechanical advantage
|
m = 20 kg
v = 2 m/s
vD = 0,5 m/s
s = 0,1 m
W1 = W3 = 40 Nm
me = (2 · 40) / 0,52 = 320 kg
FORMEL: ME = (2 · W3) / VD2
|